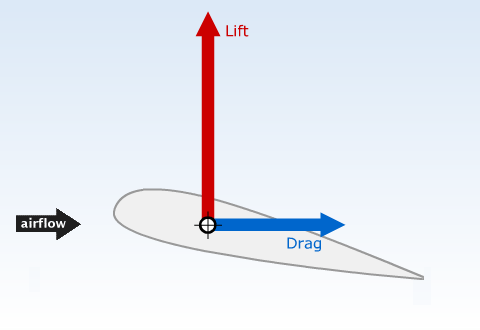
The air flow around the aerofoil has the effect of creating an upwards lift force that keeps the plane up in the air, and a backwards drag force that has the effect of slowing the plane down.
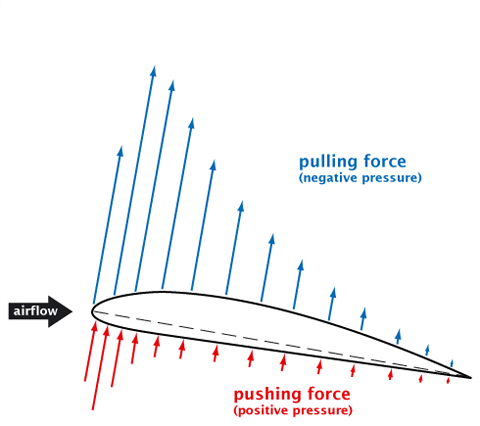
The upward lift force is created in two ways. Faster flowing air moving over the top of the aerofoil creates a negative pressure and a force pulling the wing upwards, whilst the slower air moving under the aerofoil creates a positive pressure and a pushing force on the wing.
 Drag up and down on the end of the aerofoil in this animation to change the angle of incidence and watch what happens to the lift and drag forces.
Drag up and down on the end of the aerofoil in this animation to change the angle of incidence and watch what happens to the lift and drag forces.
to see how it is related to changes in the air flow over the wing.
When an aerofoil is tilted up beyond a critical angle the air flow becomes turbulent, and the wing stalls. The sudden loss of lift in a stall makes an aeroplane difficult to control, and usually led to a crash for the early pioneers as they were flying close to the ground and did not have time to recover.
The Wright Brothers used graphs to plot the results from their experiments. This helped them to compare the performance of their foils with the designs of the other flight pioneers